What is polar night and where does it occur
There are some places on Earth where the sun does not rise above the horizon for days, weeks and even months. People go to work, raise children, and do various winter sports and outdoor activities in total darkness or with a small amount of light. In such places, the electric lighting works day and night on the street and indoors. How is that possible?
What is polar night?
Imagine you go to bed — it is dark outside, you wake up — it is still dark outside. There are only small flashes of light during the day. Such a phenomenon is called the polar night. It is a time of the year when the sun does not rise above the horizon for more than 24 hours and, accordingly, there is no natural daylight.
You can observe the polar night if you are above the Arctic circle during winter months. There's also polar night inside the Antarctic сircle, but you're not likely to be on the sixth continent of the Earth anytime soon, right? Unless, however, you are one of the active members of the Windy.app Community. For example, one of them posted some photos in the app's feed from Antarctica in the September 2021. What's in the picture? Of course, the penguins on the ice floe.
How dark it gets during this period will also depend on how close you are to the North pole. This means you won’t necessarily have 24 hours of total darkness (although most of the day can be).
Why does polar night occur?
The Earth revolves around the Sun along a certain axis, but this axis deviates slightly — about 24 degrees — several times a year, making the North and South poles alternately tilt toward the Sun. At the moment when the North pole faces the Sun, it is the polar night in the South pole, and vice versa: when the South pole faces the Sun it is dark in the North.
A reminder
By the way, recently we’ve written about another interesting phenomenon — halo. It happens when moist air manages to rise very high — more than 6 km. Here, water droplets turn into ice crystals and these crystals focus the rays so that they are directed back to you when you look at the Sun. You can read more about this phenomenon in the relevant lesson.

Fred Moon / Unsplash
What does polar night look like?
So the most of the day it is dark, but during a part of it, depending on your geographic location, it’s twilight, the interval between day and night during which the Sun is below the horizon and the light is created by the atmosphere, which diffuses light from the Sun.
Also, to understand even better what the polar night looks like, we need such a concept as True Noon. In astronomy, this is the moment in time when the sun is at its highest point — 12 pm. Putting all these concepts together, we can distinguish four types of the Polar Night:
- Civil polar night is the time of day at true noon of which the twilight is very light. It can remain this way for a long enough time, during which we can actively relax in nature without additional lighting.
- Navigational polar night is the time of day at which the main navigational stars (hence the name) are already distinguishable. At the same time, it is bright enough outside, additional lighting is needed only for any special work.
- Astronomical polar night is the most familiar time of day to us. This night is slightly brighter than usual, the moon is clearly visible in the sky — that’s why it is called so.
- Full polar night is the time of day at true noon of which there is no twilight and there is total darkness. The most interesting phenomenon, during which you can even observe the nearest galaxies.
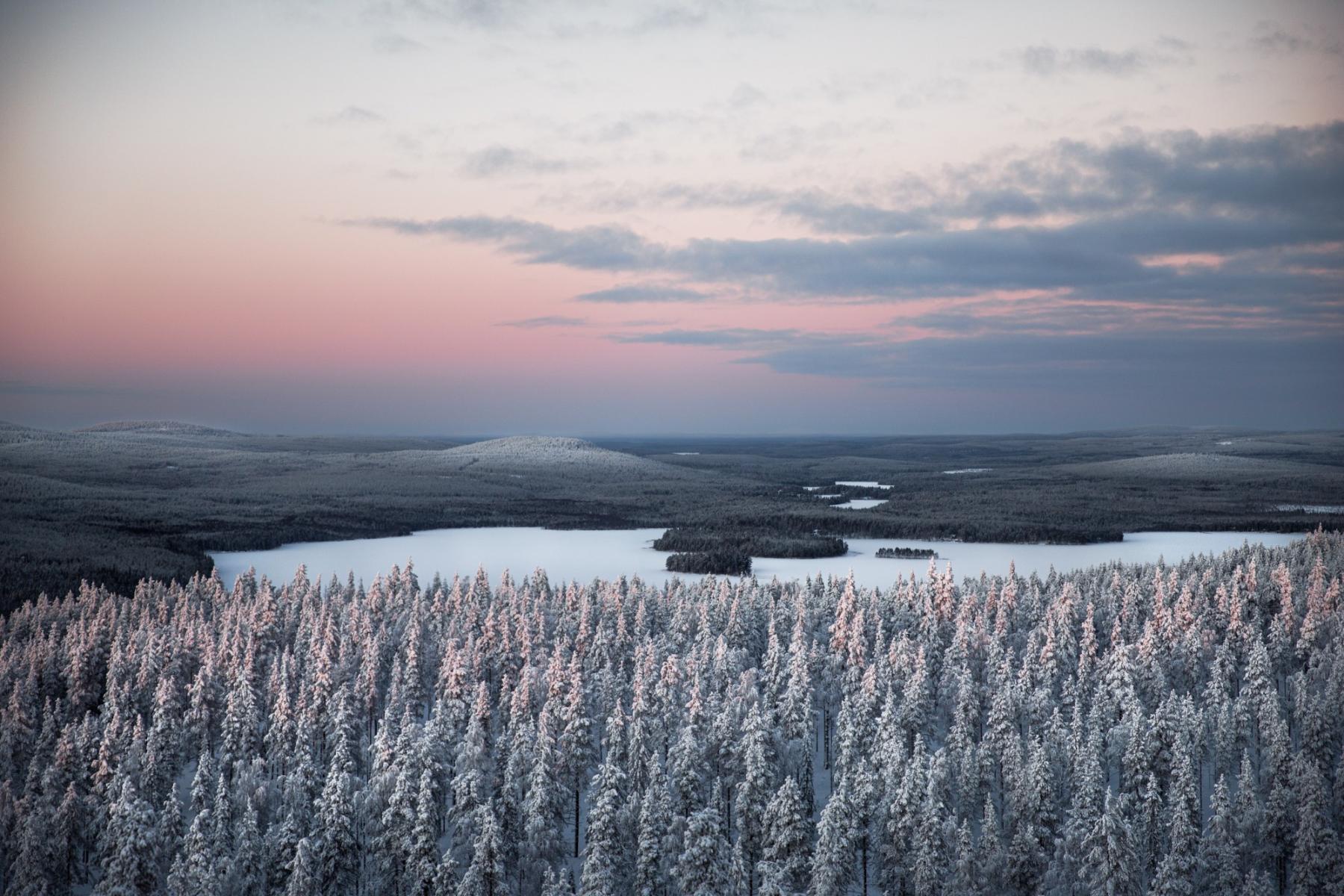

This is how the polar night looks like. Photo: Maria Vojtovicova / Unsplash
How long the polar night lasts?
The duration of the polar night depends on the latitude at which the city or town is located. Within the Arctic and Antarctic circles, it varies from zero to a few days of total darkness to 179 days or 5.9 months at the poles. At the Arctic pole the longest polar night is from September 25 to March 17. With decreasing degrees of latitude, the duration of the polar night also decreases. Here are the cities where you can observe the polar night:
- Russia. 20% of the territory! In Dickson, Krasnoyarsk Krai, the longest polar night lasts almost three months — from November 11 to February 1.
- Norway. The polar night lasts from mid-November to the end of January. The best place to observe the beauty of the Arctic night is the Svalbard Archipelago, Longyear.
- USA. Barrow is the northernmost city in the United States. It is located at latitude 76. The polar night lasts almost three months — from November 18 to January 23.
- Sweden. The northernmost city in Kiruna. The polar night lasts from December 11 to January 2.
- Greenland. The polar night lasts from mid-November to early February, about 80-85 days. During this period, the sun comes over the horizon for only a couple of hours. The best town to observe is Kanaak.
- Finland. The polar night lasts from late November to mid-January, 52-54 days. The longest night in Utsujoki is a great opportunity to observe the northern lights.
- Canada. The longest polar night lasts more than five months in the planet’s northernmost city, Alert.
How does polar night affect people?
It is believed that people living in the far north may experience difficulties with their general physical condition. At the very least, northerners during the polar night, as it is dark most of the time, have a significant decrease in household activities. People move and go for walks less, and prefer quiet rest at home.
That is why in many northern areas, for instance in Norway, there are marathons and other sports competitions aimed at encouraging people to move more, increasing their activity, and improving their health.
For example, every year in Norway there is the Polar Night Tromsøya Half Marathon, which in 2020 has attracted more than 2,500 participants, and the Arctic Snowshoe Run. The Arctic Marathon 2021 was supposed to take place from August 14 to September 14 in Vorkuta, Russia (yes, Arctic in August). However, due to the epidemiological situation, it was moved online. Anyone could pay for participation, run the chosen distance and upload the data to the site.
But it is possible to be active in the Nordic winter during the Polar Night without any competitions. Even though the conditions beyond the Arctic Circle are quite harsh, there are ski resorts almost everywhere.
For example, in Russia, in Kirovsk, there is a ski resort “Bolshoi Vudyavr”. All its tracks are equipped with artificial lighting, so as not to limit the skiing period during the polar night. Or, for example, in Finland, 170 kilometers from Rovaniemi, there is a ski resort Levi. It often hosts World Cup skiing competitions.
Where to get information about sunrise and sunset in the Windy.app?
You can find sunrise and sunset information in the Lite Weather Profile for general weather conditions.
Weather conditions and forecast for Vorkuta in the Windy.app for iOS
Information about moonrise, moonset and moon phases is also available in the app in the Fish and Fish Pro weather profiles.
Moonrise, moonset and moon phases and sunrise and sunset information in the Windy.app for iOS
If you’re going on a trip beyond the Arctic Circle in winter, the Snow Weather Profile also comes in handy — temperatures at different altitudes, snow accumulation, wind direction and speed, and so on.
Snow Weather Profile in Finland, Rovaniemi in the Windy.app for iOS
You can also find the world’s top ski resorts with information about them in the app and on the website.
Live wind map for Levi, Finland in the Windy.app for iOS
To open the profiles:
1. From the Home Screen of the app, go to the Spot Screen.
2. Select a profile by clicking on the icon to the right of the weather models. Sunrise and sunset are available right on the weather widget at the top of the screen.
3. Change the profile by going back to the profiles page.
Text: Masha Shapovalova, an author and web specialist from Moscow. Her favorite sports are kitesurfing and alpine skiing. Her articles here
Cover photo: Jonatan Pie / Unsplash
You can also find usefull
What is hail? Simple explanation
What is a brinicle — the underwater stalactite. Simple explanation
Latest News
Professional Weather App
Get a detailed online 10 day weather forecast, live worldwide wind map and local weather reports from the most accurate weather models.
Compare spot conditions, ask locals in the app chat, discover meteo lessons, and share your experience in our Windy.app Community.
Be sure with Windy.app.